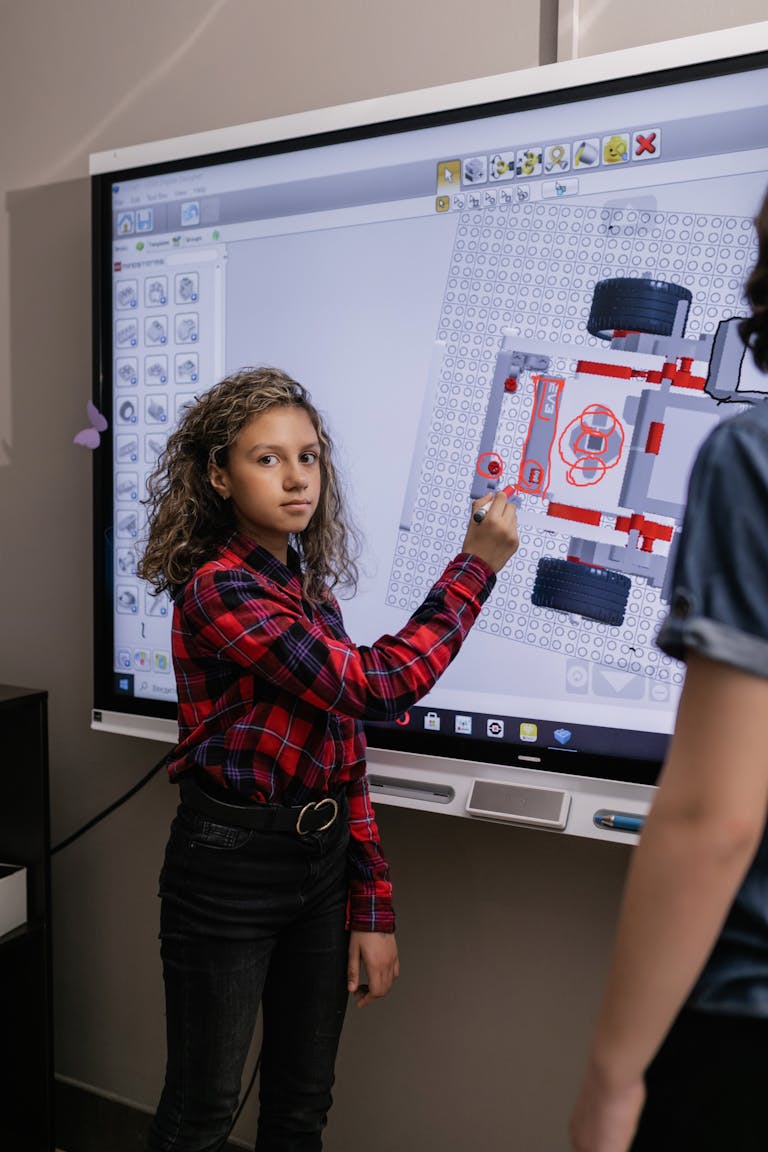
5 Tips for Teaching Students about Hardware
Understanding the structure and function of hardware is a foundational skill in computer science. Here are a few tips for teaching your students all about it!
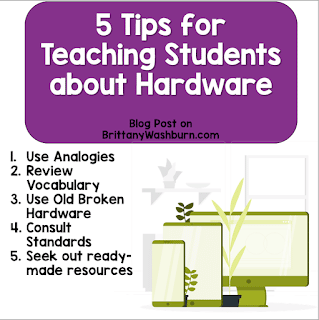
Tip #1
Use analogies.
Help your students understand the function of individual pieces of hardware by comparing them to things students are already familiar with. For example, you can compare a monitor to a window and a computer tower to a brain.
Tip #2
Review vocabulary.
Computer science is a field that has a great deal of subject specific vocabulary. Furthermore, a great deal of that vocabulary consists of words that have entirely different meanings in other contexts (port, key, mouse, etc.) Don’t assume students know the right terms for what they’re working with, or let students continue to work with technology they don’t know how to refer to correctly. Be sure to incorporate learning the definitions as well as simple item-to-word correlation, as this will enable students to begin to recognize hardware even with significant cosmetic differences (among other things).
Tip #3
Broken hardware can be your friend.
Build up a store of “dead mice”, broken keyboards and other defective hardware from wherever you can get them around your school. Bring them out for students to handle and practice with. Students can begin working on skills such as typing, maneuvering mice, plugging in usb or headphone jacks and opening and closing laptops/chromebooks without risking damage to your schools inventory of functional hardware.
Tip #4
Consult standards.
Use national computer science standards such as those put forth by CSTA or ISTE to get a clearer idea of what you should be teaching. Many hardware standards involve not only knowing how to name and correctly use hardware, but also how to troubleshoot it.
Here are a few particularly relevant guiding standards from each to start you off on the right foot:
-
1A-CS-02 K-2
Use appropriate terminology in identifying and describing the function of common physical components of computing systems (hardware).
-
1B-CS-02 3-5
Model how computer hardware and software work together as a system to accomplish tasks.
-
2-CS-02 6-8
Design projects that combine hardware and software components to collect and exchange data.
-
3A-CS-02 9-10
Compare levels of abstraction and interactions between application software, system software, and hardware layers.
-
1 Empowered Learner:
1b – Students build networks and customize their learning environments in ways that support the learning process.
1d – Students understand the fundamental concepts of technology operations, demonstrate the ability to choose, use and troubleshoot current technologies and are able to transfer their knowledge to explore emerging technologies.
-
4 Innovative Designer:
Students use a variety of technologies within a design process to identify and solve problems by creating new, useful or imaginative solutions.
-
6 Creative Communicator:
6a – Students choose the appropriate platforms and tools for meeting the desired objectives of their creation or communication.
Tip #5
Don’t do work that you don’t have to.
My shop contains lessons ready-made for you to teach the Parts of a Computer in various themes, Computer Fundamentals, and more!
Check out these eBooks that teach students about computer basics, including hardware:
Computer hardware vocabulary to teach students:
- Computer: A machine that can be used to store and process information.
- Keyboard: A device with buttons or keys that can be pressed to input letters, numbers, and other characters into a computer.
- Mouse: A device that moves a cursor on the screen when it is moved on a desk or other surface, allowing the user to interact with the computer.
- Monitor: A screen that displays information, images, and videos from the computer.
- CPU: The Central Processing Unit is the part of the computer that carries out instructions and performs calculations.
- Printer: A device that can print text and images onto paper.
- Headphones: A device that allows the user to listen to sound from the computer without disturbing others.
- Webcam: A camera that can be used to take pictures or record video, often used for video chatting or online meetings.
- Speakers: Devices that output sound from the computer, allowing the user to hear music, videos, and other audio content.
- USB drive: A small device that can be plugged into a computer to store and transfer data, such as documents, photos, and videos.
Pin this post to get back to later: